What is Silymarin (Milk Thistle P.E.)?
Silymarin is a mixture of flavonoids and lignins extracted from the seeds of milk thistle.
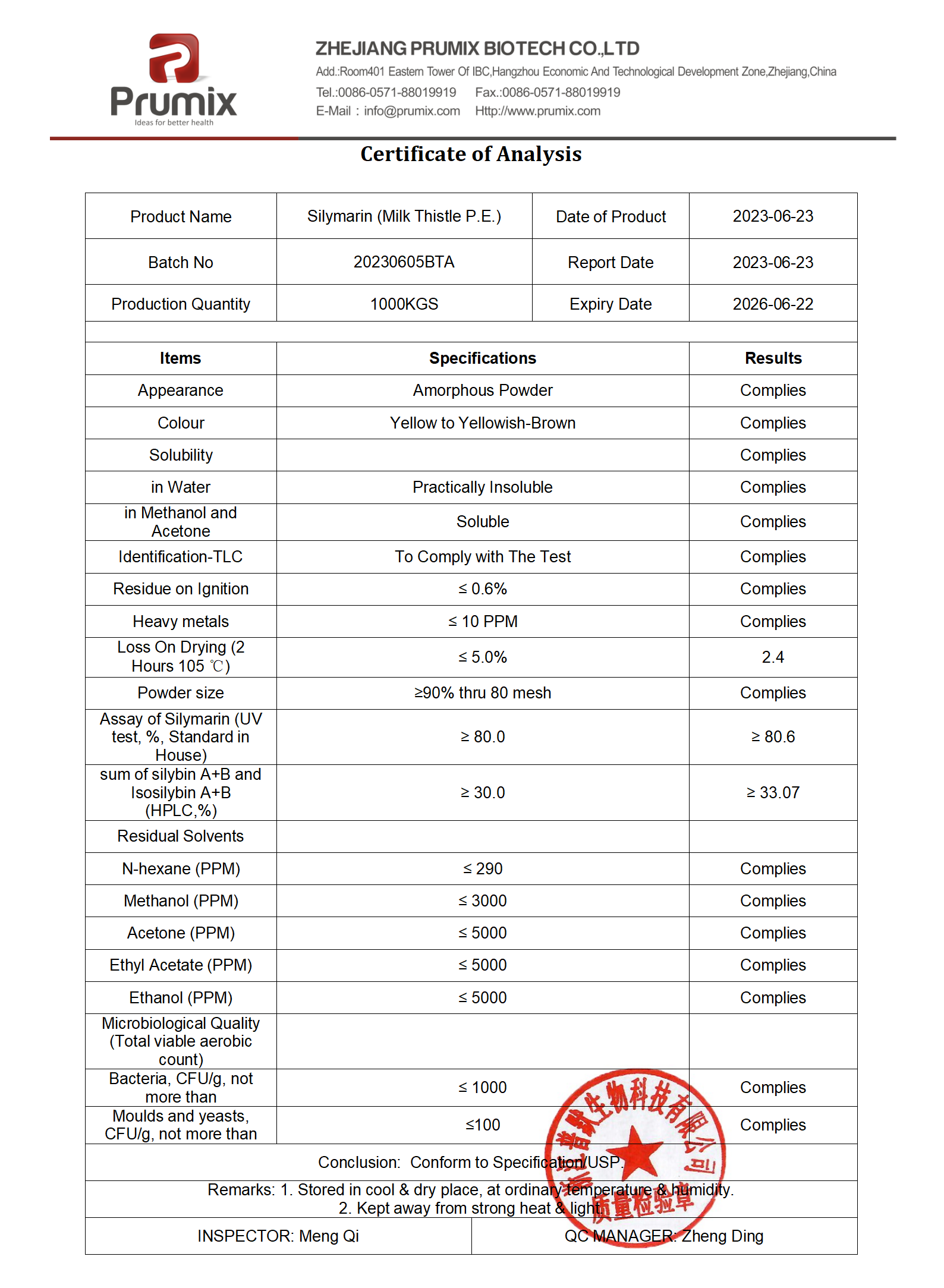
Product Name: Silymarin
CAS No.: 65666-07-1
Molecular Formula: C25H22O10
Molecular Weight: 482.44
EINECS No.: 613-830-9
China Factory: Zhejiang Prumix Biotech CO., Ltd.
Introduction:
Silymarin, also known as Yiganling, Ligantai, Xilimarin, and Liganlong, is a flavonoid complex extracted from the seeds of the Asteraceae plant Silybum marianum, which is a condensation product of dihydroflavonol and phenylpropanoid derivatives. It is yellow powder or crystalline powder in appearance and tastes bitter. It is easily soluble in acetone, ethyl acetate, methanol and ethanol, slightly soluble in chloroform, and almost insoluble in water. It has a strong liver-protecting effect and can protect liver cells from free radical damage. It is much more effective than vitamin E, promotes protein synthesis, accelerates the production of new liver cells, and allows damaged liver cells to repair themselves, so it is called a "natural liver-protecting drug."
Main ingredients:
Since milk thistle is difficult to dissolve in water, silymarin is extracted and used as a main ingredient. Silymarin is a general term for a series of brass lignin compounds extracted from the fruit of the asteraceae plant milk thistle. The main ingredients include silybin, silybinin, silybin and isosilybin, among which silybin has the highest content and the highest activity.
Efficacy and effects:
Milk thistle is an excellent liver-protecting plant. Its seeds contain new flavonoids, the main component of which is SILYMARIN, a mixture of silybin-glycosides, and are rich in fat-soluble vitamins A, D, and E. It has good antioxidant function, can effectively remove free radicals, and "break" the damage caused by multi-enzyme reactions to the body, and has a very good detoxification function for the liver. It has a good health care effect on various liver and gallbladder symptoms such as cirrhosis, fatty liver, liver poisoning, cholecystitis, cholecystitis, and pain caused by cholelithiasis.
Main effects:
1. Prevent liver damage: Form a protective film on liver cells, significantly reduce the damage to the liver caused by excessive alcohol.
2. Assist liver disease: It has a strengthening and repairing effect on the liver. By stimulating protein synthesis, it can promote liver cell repair and promote cell regeneration. It has a significant improvement in the symptoms and liver function of hepatitis patients.
3. It can reduce the chance of liver cells being damaged by free radicals and protect liver cell membranes. It has an anti-radiation effect.
4. Regulates bile secretion, helps digest fat, and nourishes the stomach, spleen, gallbladder, and kidneys.
5. Provides nutrition to the circulatory system and reduces cardiovascular problems, including atherosclerosis and hypercholesterolemia.
.png)